Consumer behavior is the study of individuals, groups, or organizations and the processes they use to select, secure, use, and dispose of products, services, experiences, or ideas to satisfy needs and the impacts that these processes have on the consumer and society 1. It encompasses a wide range of disciplines, including psychology, sociology, economics, and anthropology, to gain a comprehensive understanding of how and why consumers make decisions. This exploration delves into the intricacies of consumer behavior, examining its definition, influential factors, prominent models, and practical applications in marketing and business.
Defining Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior aims to understand the “why” and “how” behind consumer actions. It seeks to explain not just what consumers buy, but also why they buy it, how they use it, and how they dispose of it 1. This involves examining various aspects of consumer interaction with products and services, including:
- Purchase behavior: This encompasses when, where, and how consumers make purchases, including their preferred channels (online, in-store), payment methods, and shopping frequency 2.
- Product usage: This examines how often and in what ways consumers use a product or service, as well as their level of satisfaction with it 2.
- Product disposal: This considers how long consumers retain a product and their methods of disposal, such as recycling, reselling, or discarding 2.
Types of Consumer Behavior
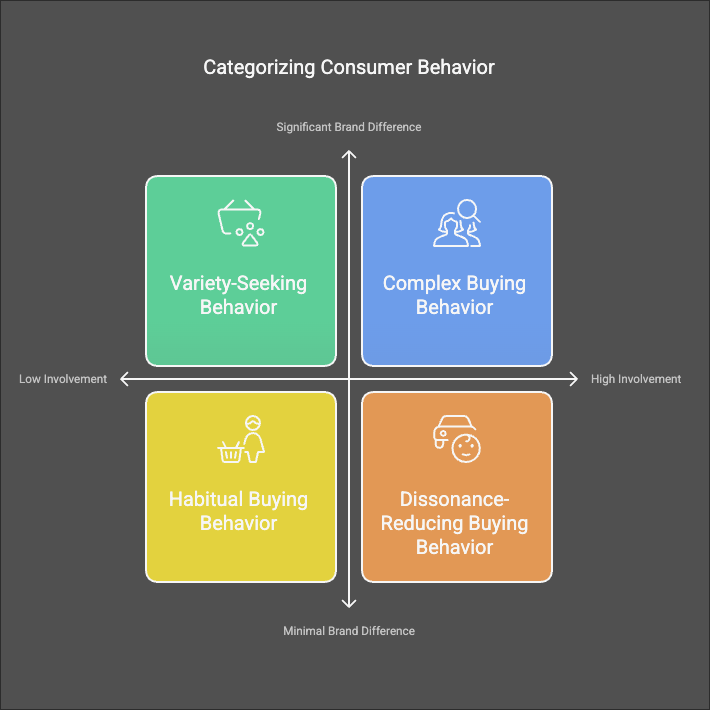
Consumers exhibit different buying behaviors depending on their level of involvement in the purchase decision and the perceived differences between brands 3. Four main types of consumer behavior have been identified:
- Habitual buying behavior: This involves routine purchases with low consumer involvement and minimal difference between brands. Consumers typically stick to familiar brands out of habit or convenience 3.
- Variety-seeking behavior: In this type, consumers have low involvement but perceive significant differences between brands. They often switch brands to experience new options and avoid boredom 3.
- Dissonance-reducing buying behavior: This occurs when consumers are highly involved in a purchase but see little difference between brands. They may experience anxiety about making the wrong choice and seek reassurance after the purchase 3.
- Complex buying behavior: This type involves high consumer involvement and significant perceived differences between brands. Consumers engage in extensive information search and evaluation before making a purchase, often for expensive or infrequent purchases 3.
Theoretical Perspectives on Consumer Behavior
Several theoretical perspectives provide frameworks for understanding consumer behavior:
- Psychoanalysis: This approach, rooted in the work of Sigmund Freud, suggests that consumers’ unconscious psychological urges, such as hidden hopes, fears, and motivations, influence their purchasing behavior 4.
- Socio-psychology: This perspective, associated with Thorstein Veblen, posits that a consumer’s cultural and social background significantly shapes their buying decisions, often driven by the need to maintain social status 4.
- Reasoned action: This theory proposes that consumers assess products or services before making a decision, considering their attitudes towards the item and the perceived social approval of their choice 4.
- Impulse buying: This theory, developed by Hawkins Stern, suggests that impulse purchases are driven by external forces like discounts, promotions, peer influence, or perceived quality rather than careful consideration 4.
- Maslow’s hierarchy of needs: This theory proposes that human needs are prioritized in a hierarchical order, starting with basic survival needs and progressing to higher-level needs like self-actualization. Consumers prioritize purchases that fulfill their most pressing needs 4.
Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, both internal and external. These factors can be categorized as follows:
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors involve the inner workings of the consumer’s mind and how they process information and make decisions. Key psychological factors include:
- Motivation: This refers to the internal drives that compel consumers to take action, often stemming from unmet needs or desires 5.
- Perception: This involves how consumers select, organize, and interpret information from their environment. It includes processes like selective attention, selective distortion, and selective retention 5.
- Learning: This refers to changes in consumer behavior resulting from experiences and acquired knowledge. Consumers learn through trial and error, observation, and information gathering 5.
- Attitudes and Beliefs: These are learned predispositions to respond to an object or idea in a favorable or unfavorable way. They are shaped by personal experiences, social interactions, and exposure to marketing messages 6.
- Framing and Subtle Cues: Even small changes in wording or presentation can significantly influence consumer behavior. For example, research by Dr. Robert Cialdini showed that adding the phrase “Every penny will help” to a donation request nearly doubled the likelihood of people donating 7.
Social Factors
Social factors encompass the influence of other people and social groups on consumer behavior. These include:
- Family: Family members often have a strong influence on consumer choices, particularly in household purchases and decisions related to children’s products 6.
- Reference Groups: These are individuals or groups that consumers identify with or aspire to be like. They can influence product choices, brand preferences, and even lifestyle decisions 6.
- Social Status: This refers to an individual’s position within society, often associated with income, education, and occupation. It can influence preferences for certain brands, products, and consumption patterns 5.
- Culture and Subculture: These encompass the shared values, beliefs, and customs within a society or a specific group within that society. They can significantly impact consumer preferences, product choices, and even the meaning associated with certain brands or products 5.
- Consumer Ethnocentrism: This refers to the tendency to favor products from one’s own culture over those from other cultures. It can influence brand preferences and purchase decisions based on national identity and cultural values 8.
- Authenticity and Connection: Consumers are increasingly seeking authenticity and a connection with brands. They value brands that are transparent, reflect their values, and engage with them on a personal level 9.
- Social-Cognitive Theory: This theory emphasizes the interplay of personal and environmental factors in shaping consumer behavior. It suggests that individuals learn through observation and social interaction, and their behavior is influenced by both their own cognitive processes and the social context in which they operate 10.
Personal Factors
Personal factors are unique to each individual and influence their preferences and choices. These include:
- Age and Life-Cycle Stage: Consumer needs and preferences evolve throughout the life cycle, from childhood to old age. For example, a teenager might prioritize trendy clothing, while an older adult might focus on health and wellness products 5.
- Occupation and Lifestyle: A person’s job and lifestyle can significantly influence their product choices and consumption patterns. A busy professional might opt for convenience foods, while an outdoor enthusiast might invest in specialized sporting equipment 5.
- Personality: Individual traits and characteristics, such as introversion/extroversion, openness to experience, and conscientiousness, can shape how consumers perceive and interact with the world, influencing their brand preferences, product choices, and shopping styles 5.
Economic Factors
Economic factors relate to a consumer’s financial situation and the broader economic environment. These include:
- Personal Income: A consumer’s disposable income directly affects their purchasing power and ability to afford certain products or services 5.
- Economic Conditions: Macroeconomic factors, such as inflation, recession, or economic growth, can influence consumer spending patterns and preferences for certain types of products 5.
Technological Factors
Technological advancements have a profound impact on consumer behavior, shaping how consumers access information, interact with brands, and make purchase decisions. Key technological factors include:
- Technological Advancements: The rapid pace of technological innovation introduces new products, services, and ways of interacting with brands. For example, the rise of smartphones has transformed how consumers shop, access information, and make purchase decisions 11.
- Digital Platforms: The rise of digital platforms, such as online shopping websites, social media, and mobile apps, has revolutionized consumer behavior. Consumers now have access to a vast amount of information, can easily compare products and prices, and are influenced by online reviews and social media trends 1.
- Targeted Advertising: Technology enables businesses to deliver personalized advertising messages to specific consumer segments based on their online behavior, demographics, and interests. This has increased the effectiveness of advertising and its influence on consumer choices 1.
Analyzing Consumer Behavior
To understand consumer behavior, businesses and researchers employ various methods to gather and analyze data. This involves collecting both qualitative and quantitative data to gain a comprehensive view of consumer preferences, motivations, and decision-making processes 12. Some common methods include:
- Surveys: These involve collecting data from a sample of consumers through questionnaires or interviews. Surveys can gather quantitative data on demographics, purchase behavior, and product preferences, as well as qualitative data on consumer attitudes and opinions.
- Focus Groups: These involve moderated discussions with small groups of consumers to explore their perceptions, opinions, and experiences with a product or service. Focus groups provide valuable qualitative insights into consumer behavior.
- Observational Studies: These involve observing consumer behavior in natural settings, such as stores or online platforms. Observational studies can provide insights into how consumers interact with products, make decisions, and navigate shopping environments.
By combining qualitative and quantitative data from these various methods, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of consumer behavior and develop more effective marketing strategies.
Consumer Behavior Models
Consumer behavior models provide frameworks for understanding the decision-making processes that consumers undergo before, during, and after a purchase. These models help marketers predict and influence consumer behavior by identifying key stages and factors involved in the buying process. However, it’s important to acknowledge the challenges and limitations of customer behavior modeling. Building accurate models can be complex and expensive, and they may not always capture the full complexity of consumer decision-making 13. Some prominent models include:
Engel-Kollat-Blackwell (EKB) Model
The EKB model outlines a five-stage process that consumers typically go through when making a purchase decision 14:
- Problem Recognition: The consumer recognizes a need or want.
- Information Search: The consumer seeks information about potential solutions.
- Evaluation of Alternatives: The consumer compares different products or brands.
- Purchase Decision: The consumer makes a choice and completes the purchase.
- Post-Purchase Evaluation: The consumer assesses their satisfaction with the purchase.
This model highlights the importance of understanding consumer needs at each stage and providing relevant information and support to guide them towards a purchase decision.
Black Box Model
The Black Box model focuses on the external stimuli that influence consumer behavior, such as marketing messages, product features, and pricing strategies 14. It acknowledges that the internal psychological processes that drive consumer decisions are complex and often difficult to observe directly. By understanding the relationship between external stimuli and consumer responses, marketers can optimize their marketing efforts to elicit desired behaviors.
Hawkins-Stern Impulse Buying Model
This model focuses specifically on impulse purchases, which are often triggered by external stimuli such as product displays, promotions, or social influence 14. It categorizes impulse buying into four types:
- Pure impulse: A spontaneous urge to buy.
- Reminder impulse: Triggered by seeing a product and remembering a need.
- Suggestion impulse: Influenced by a suggestion from another person.
- Planned impulse: A general intention to buy a product type, with the specific decision made on impulse.
Understanding these different types of impulse buying can help retailers and marketers design effective strategies to capitalize on spontaneous purchase decisions.
Howard Sheth Model
The Howard Sheth model differentiates between three levels of consumer decision-making based on product familiarity and purchase frequency 15:
- Extensive problem-solving: For unfamiliar or complex products, involving significant information search and evaluation.
- Limited problem-solving: For familiar products purchased occasionally, involving less extensive information search.
- Habitual decision-making: For routine purchases, involving minimal effort and evaluation.
This model highlights the importance of tailoring marketing strategies to the specific decision-making process consumers are likely to engage in.
Applications of Consumer Behavior in Marketing and Business
Understanding consumer behavior is crucial for businesses to effectively market their products and services, build strong customer relationships, and achieve sustainable growth. Some key applications include:
Market Segmentation
By understanding the diverse needs and preferences of consumers, businesses can segment their target audience into distinct groups with similar characteristics. This allows for more targeted and effective marketing campaigns that resonate with specific consumer segments 16. Market segmentation involves grouping buyers based on various factors, such as demographics, geographic location, buying habits, or psychological factors 17. This targeted approach allows marketers to tailor their messages and offerings to specific consumer groups, increasing the effectiveness of their campaigns.
Product Development and Innovation
Insights into consumer behavior can guide product development by identifying unmet needs, desired features, and preferences for product design and functionality. This helps companies create products that are more likely to succeed in the marketplace 18.
Pricing Strategies
Understanding consumer price sensitivity and perceptions of value can help businesses set optimal prices for their products or services. This includes considering factors such as perceived quality, competitor pricing, and consumer willingness to pay 18.
Promotion and Advertising
By understanding how consumers process information and respond to different types of marketing messages, businesses can create more effective advertising campaigns. This includes tailoring messages to specific consumer segments, using persuasive communication techniques, and selecting appropriate channels to reach the target audience 18.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Consumer behavior insights can help businesses build stronger customer relationships by understanding customer needs, preferences, and expectations. This includes personalizing interactions, providing excellent customer service, and developing loyalty programs that reward repeat purchases 18.
Retail Strategy
Understanding how consumers navigate retail environments, what attracts their attention, and how they make purchase decisions can help retailers optimize store layouts, product placement, and in-store marketing to enhance the shopping experience and drive sales 18.
Public Policy and Social Marketing
Governments and non-profit organizations can use consumer behavior insights to design public policies and social marketing campaigns that promote positive behaviors and address social issues. This includes campaigns to encourage healthy eating, recycling, or safe driving 18.
Crisis Management and Reputation Management
Consumer behavior knowledge is crucial in managing crises and protecting brand reputation. Understanding consumer sentiment and behavior during times of crisis or negative publicity allows businesses to implement effective communication and recovery strategies 19. This involves monitoring social media, responding to consumer concerns, and taking appropriate action to rebuild trust and mitigate damage to the brand’s image.
Personalization and Customization
The increasing availability of consumer data and advancements in technology have led to a growing emphasis on personalization in marketing. By understanding individual consumer preferences, businesses can tailor their marketing messages, product recommendations, and overall customer experience to specific needs and desires 9. This personalized approach can enhance customer satisfaction, foster loyalty, and drive sales.
Conclusion
Consumer behavior is a dynamic and multifaceted field that is essential for businesses to understand in order to achieve success in today’s marketplace. By understanding the factors that influence consumer choices, the decision-making processes involved, and the various models that explain these processes, businesses can develop more effective strategies to meet consumer needs, build strong customer relationships, and achieve sustainable growth. The evolving nature of consumer behavior, driven by technological advancements, social trends, and economic shifts, requires ongoing research and analysis for businesses to stay ahead of the curve and maintain a competitive edge. Moreover, ethical considerations are paramount in applying consumer behavior knowledge, particularly in areas like personalized marketing and influencer marketing, to ensure responsible and transparent practices that respect consumer privacy and autonomy. By integrating consumer-centric approaches and ethical considerations into their strategies, businesses can foster trust, build long-term relationships with their customers, and contribute to a more sustainable and responsible marketplace.
Works cited
1. Consumer Behavior: Trends, Types, and Tactics – NIQ, accessed January 26, 2025, https://nielseniq.com/global/en/info/consumer-behavior/
2. Consumer Behavior: Definition, Types, & Influences | SurveyMonkey, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.surveymonkey.com/mp/consumer-behavior/
3. Consumer Behavior Archives | American Marketing Association, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.ama.org/topics/consumer-behavior/
4. Consumer behavior guide for businesses – Zendesk, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.zendesk.es/blog/consumer-behavior/
5. 5 Major Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior – Shiksha Online, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.shiksha.com/online-courses/articles/5-major-factors-influencing-consumer-behavior/
6. What factors influence consumer behavior? – Product Marketing Alliance, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.productmarketingalliance.com/what-influences-customer-behavior/
7. Understanding Consumer Behavior to Convert More Customers – Help Scout, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.helpscout.com/consumer-behavior/
8. Analysis of Consumer Behaviour in the Context of the Place of Purchasing Food Products with Particular Emphasis on Local Products – PubMed Central, accessed January 26, 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9915062/
9. 16 Big Shifts In Consumer Behavior That Are Impacting Marketing Today – Forbes, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbesagencycouncil/2024/06/27/16-big-shifts-in-consumer-behavior-that-are-impacting-marketing-today/
10. Social marketing: 3.2 The factors which influence consumer behaviour | OpenLearn, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.open.edu/openlearn/money-business/business-strategy-studies/social-marketing/content-section-3.2
11. What are the 6 factors influencing consumer behavior? – Clootrack, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.clootrack.com/knowledge-base/major-factors-influencing-consumer-behavior
12. The Complete Consumer Behavior Analysis Guide – Quid, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.quid.com/knowledge-hub/resource-library/blog/consumer-behavior-analysis/
13. Customer Behavior Modeling & Analysis | Optimove, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.optimove.com/resources/learning-center/customer-behavior-modeling
14. 12 Customer Behavior Models: How They Impact Your Business – Userpilot, accessed January 26, 2025, https://userpilot.com/blog/customer-behavior-model/
15. 10 Consumer Behaviour Models Types and Stages – Nudge, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.nudgenow.com/blogs/consumer-behaviour-models-types-stages
16. Applications of Consumer Behaviour in Marketing • MBA Notes by TheMBA.Institute, accessed January 26, 2025, https://themba.institute/consumer-behaviour/applications-of-consumer-behaviour-in-marketing/
17. Consumer Behavior: Understanding Your Market – Keiser University, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.keiseruniversity.edu/consumer-behavior-understanding-your-market/
18. 1.c Application of Consumer Behavior – College Hive, accessed January 26, 2025, https://collegehive.in/docs/5th_sem/site/CBNM/Module_01_Introduction_to_Consumer_Behavior/1.c_Application_of_Consumer_Behavior.html
19. Applications of Consumer Behavior Knowledge in Marketing – Easy Notes Store, accessed January 26, 2025, https://easynotesstore.com/applications-of-consumer-behavior-knowledge-in-marketing/
20. 6 Major Factors Influencing Consumer Buying Behaviour – Nudge, accessed January 26, 2025, https://www.nudgenow.com/blogs/factors-affecting-consumer-buying-behaviour-overview



You must be logged in to post a comment.